ملف:Male-Female suicide ratios and rates 2015 (age-standardized).svg

الملف الأصلي (ملف SVG، أبعاده 512 × 327 بكسل، حجم الملف: 3٫76 ميجابايت)
| هذا ملف من ويكيميديا كومنز. معلومات من صفحة وصفه مبينة في الأسفل. كومنز مستودع ملفات ميديا ذو رخصة حرة. |
ملخص
| الوصفMale-Female suicide ratios and rates 2015 (age-standardized).svg |
English: Male–Female ratios of suicide rates in 2015. Data by World Health Organization (rev. April 2017): global average 1.7 : 1 is used as a reference (men were 70% more likely than women to die by suicide). Below, male (left) and female (right) age-standardizedα suicide mortality rates per 100,000 individuals used to derive the above ratios.
Global average was as higher as 1.9 in year 2012 according to the WHO, and 2.0 according to the IHME.[1] Mortality data is always estimated at a degree. Gender differences in suicide are described since the 1990s, by traditionally higher male suicide rates as contraposed to a typical disproportion of females in nonfatal suicide behavior; a relevant review of previous years' data later mentioned throughout the 2000s, noted this male/female disproportion in suicidality throughout Western countries: the proportion of male suicides was incongruous with that of female suicide attempts, as the male-female ratio of suicides was above 2.4 meaning males completed suicide at least 140% more than females, while the female-male ratio of suicide attempts was 1.5 meaning females attempted suicide 50% more than males.[2][3] Cited as 'gender paradox of suicidal behavior', it is essentially attributed to post-industrial sociocultural influences and gendered identities: females being more vulnerable to psychological problems and receptive to psychotherapeutic approaches (in western societies mental-health disorders are 20-40% higher in women than men, and female therapists outnumber male) particularly at a young age, report suicide ideation and attempt more frequently and are allowed to discuss their emotions, but males being required to express strength and stoicism assuming social status and working roles crucial for their identity are less likely to seek help for suicidal feelings. Since nonfatal suicidal behavior is typically higher in females while suicide rates are traditionally higher for males, then male vulnerability to suicidal behavior is often explained in terms of higher lethality of suicide methods used and hopelessness, being nevertheless that stigmatization of suicidal behaviors tends to frame surviving a suicidal act and seeking help for mental distress as something ‘inappropriate’ for men: research suggests that the gender gap is partially a result of the choice of more lethal methods and the experience of more aggression, which rather provide an indication of the higher intent to die in men.[4][5][6][7] This gender gap holds true in western cultures, while narrows elsewhere, unto where these patterns are contradicted entirely in various Asian societies (counting almost half of global population). Indeed gender differences in suicide vary significantly among countries: western societies (cultural heritage of european origin, such as european languages or religion) report a higher male mortality by suicide than any other, while South and East Asian a much lower, with China accounting for the greatest number of female suicides. 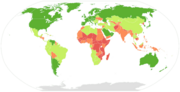 Wealth is also a constant, being that the gender gap is generally limited or non-existent in low- and middle-income societies, whereas it is never absent in high-income countries (depicted in darker green aside): 200,000 deliberately take their own life in Europe and the Americas every year, about 40,000 females and 150,000 males.[8][9][10] The problem then is not the old-fashioned question — why do so many women commit suicide in China; the actual question is why do so many men commit suicide in high-income countries?[11] In the last 45 years suicide rates have increased by 60% worldwide. An estimated one million people per year die by suicide or a death every 40 seconds or about 3,000 every day (more people die from suicide than from murder and war). At the same time, nonfatal episodes are reported up to 20 times as much, with female adolescents and minority groups (migrants, transgenders, etc.) bearing most relevant socio-economic implications for suicide prevention.[12][13][14]
Late 1890s recorded first gender-related observation on suicide by Émile Durkheim: according to statistics of the time, more men died of suicide than women every year. Also, Durkheim mentioned relations between western industrialization, modern communities and vulnerability to self-destructive behavior, suggesting social norms and pressures have effects on suicide.[10][19] Reinforcement of male gender roles such as strength, independence, risk-taking behavior, often prevents males from seeking help for suicidal feelings and depression.[20][21] It is observed that shifting cultural attitudes about gender roles and social norms and especially ideas about masculinity, may also contribute to closing the gender gap.[5][7][22] Suicidal behavior is also subject of study for economists since about the 1970s: although national costs of suicide and suicide attempts (up to 20 for every one completed suicide) are very high, suicide prevention is hampered by scarce resources for lack of interest by mental health advocates and legislators; and moreover, personal interests even financial are studied with regards to suicide attempts for example, in which insights are given that often "individuals contemplating suicide do not just choose between life and death [..] the resulting formula contains a somewhat paradoxical conclusion: attempting suicide can be a rational choice, but only if there is a high likelihood it will cause the attempter's life to significantly improve."[23][24] In the United States alone, yearly costs of suicide and suicide attempts are comprised in 50-100 billion dollars.[25][26]
Social stigma is considered as well a "major barrier" to suicide prevention, and "the underlying motive for discrimination [..] caused by lack of knowledge - ignorance [..] One extreme example is the criminalization of suicidal behaviour, which still occurs in many countries."[28][29] Per recent releases, the World Health Organization warns about social stigma towards suicidal behavior and psychiatric patients, and the taboo to openly discuss suicide, representing to date challenges and obstacles for suicide prevention policies along with low availability and quality of data.[27]
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| التاريخ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| المصدر |
Based on
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| المؤلف | multiple | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| إصدارات أخرى |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ترخيص
| هذا الملف متوفر تحت ترخيص المشاع الإبداعي CC0 1.0 الحقوق العامة. | |
| لقد وَضَعَ صاحب حقوق التَّأليف والنَّشر هذا العملَ في النَّطاق العامّ من خلال تنازُلِه عن حقوق العمل كُلِّها في أنحاء العالم جميعها تحت قانون حقوق التَّأليف والنَّشر، ويشمل ذلك الحقوق المُتَّصِلة بها والمُجاورة لها برمتها بما يتوافق مع ما يُحدده القانون. يمكنك نسخ وتعديل وتوزيع وإعادة إِنتاج العمل، بما في ذلك لأغراضٍ تجاريَّةٍ، دون حاجةٍ لطلب مُوافَقة صاحب حقوق العمل.
http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.enCC0Creative Commons Zero, Public Domain Dedicationfalsefalse |
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| أنا، مالِك حقوق تأليف ونشر هذا العمل، أجعله في النِّطاق العامِّ، يسري هذا في أرجاء العالم كلِّه. في بعض البلدان، قد يكون هذا التَّرخيص غيرَ مُمكنٍ قانونيَّاً، في هذه الحالة: أمنح الجميع حق استخدام هذا العمل لأي غرض دون أي شرط ما لم يفرض القانون شروطًا إضافية. |
الشروحات
العناصر المصورة في هذا الملف
يُصوِّر
قيمة ما بدون عنصر ويكي بيانات
١٠ أغسطس 2018
image/svg+xml
تاريخ الملف
اضغط على زمن/تاريخ لرؤية الملف كما بدا في هذا الزمن.
| زمن/تاريخ | صورة مصغرة | الأبعاد | مستخدم | تعليق | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| حالي | 04:23، 7 مارس 2021 |  | 512 × 327 (3٫76 ميجابايت) | HomemMédio | See post at https://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/User_talk:HomemM%C3%A9dio for a lengthier summary (because of the character limit here) - in simple words, last week SuperSucker recalled about map building, that maps look better and more reputable when free from graphic inclusions (such as legends and typings). |
| 05:15، 27 فبراير 2021 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | PerformedMixedBoated | better legend - original author was banned before being able to do it himself | |
| 13:46، 31 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫8 ميجابايت) | NoTengoFriends | better legend - original author confided me he was never able to make the smaller legend more legible himself | |
| 21:59، 19 ديسمبر 2020 | 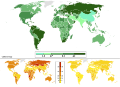 | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | NoTengoFriends | Reverted to version as of 05:10, 7 December 2020 (UTC) For spirit of diversity and inclusion, one of the triple maps is good kept green. | |
| 22:33، 14 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | MedicalWorker | above 4.0 countries were blue a bit too deep | |
| 22:51، 13 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | MedicalWorker | blue too deep | |
| 08:21، 13 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | MedicalWorker | more in line with the original author's perspective of distinguishing between below average and above average countries | |
| 07:34، 13 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | MedicalWorker | legend | |
| 07:13، 13 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | MedicalWorker | homogeneity too excessive - by the way, this map was put together during the brexit years and anti-EU climate, and as per the author's own admission at his talk page, it's gone through an excessive european political interest from EU parties (even affecting his personal life apparently), which is probably why he was forced to pick green as the main color rather than the obvious blue, hopefully he enjoys this change to blue as well | |
| 20:18، 12 ديسمبر 2020 |  | 512 × 369 (3٫79 ميجابايت) | MedicalWorker | color quieter |
استخدام الملف
الصفحة التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
الاستخدام العالمي للملف
الويكيات الأخرى التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
- الاستخدام في ba.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام في en.wikipedia.org
- الاستخدام في www.wikidata.org
بيانات وصفية
هذا الملف يحتوي على معلومات إضافية، غالبا ما تكون أضيفت من قبل الكاميرا الرقمية أو الماسح الضوئي المستخدم في إنشاء الملف.
إذا كان الملف قد عدل عن حالته الأصلية، فبعض التفاصيل قد لا تعبر عن الملف المعدل.
| العرض | 100% |
|---|---|
| الارتفاع | 100% |

